Enzymes Are Not Consumed In Chemical Reactions What Does This Mean
Enzymes are biological catalysts. This is because they do not change the free energy of the reactants or products.
In a catalyzed reaction the catalyst generally enters into chemical combination with the reactants but is ultimately regenerated so the amount of catalyst remains unchanged.

Enzymes are not consumed in chemical reactions what does this mean. They do not get consumed in the chemical reactions that they accelerate. Well technically they give an alternative pathway for a reaction to happen and are used up at some point but then a second chemical reaction with the alternative pathway creates the catalyst molecule again and. Outside of this zone they are less effective.
However enzymes do differ from most other catalysts in that they are highly specific for their substrates. Enzymes are known to catalyze about 4000 biochemical reactions. Enzymes are not reactants and are not used up during the reaction.
Enzymes act as biocatalysts and is not consumed in the reaction. Each enzyme typically binds only one substrate. As with all catalysts enzymes are not consumed by the reactions they catalyze nor do they alter the equilibrium of these reactions.
The biological processes that occur within all living organisms are chemical reactions and most are regulated by enzymes. Cells use a lot of energy. Instead they are available to bind new substrates and catalyze the same reaction repeatedly.
Enzymes are not consumed during a reaction. It is not permanently changed by the reaction it catalyzes c. Increasing substrate concentration also increases the rate of reaction to a certain point.
The fact that they arent changed by participating in a reaction distinguishes catalysts from substrates which are the reactants on which catalysts work. In other words they are not used up by the reaction and can be re-used. It increases the rate of a chemical reaction.
Once an enzyme binds to a substrate and catalyzes the reaction the enzyme is released unchanged and can be used for another reaction. Why do cells need a catalyst. Thereof why do enzymes generally bind to only one type of substrate quizlet.
This means that for each reaction there does not need to be a 11 ratio between enzyme and substrate molecules. It is important to remember that enzymes do not change whether a reaction is exergonic spontaneous or endergonic. Chemically enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction.
There are thousands of reactions that take place in cells and these require energy. Exergonic Spontaneous Coupling of blank reactions contribute to pathways. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific.
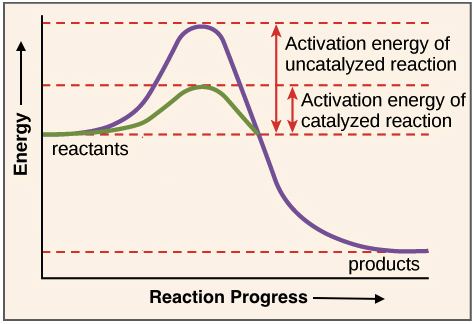
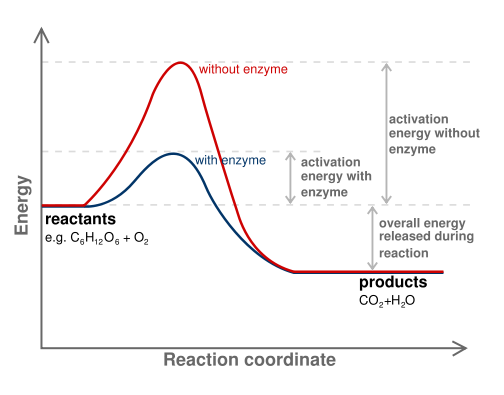
How does substrate concentration affect enzyme activity experiment. Enzymes lower the activation energy of the reaction but do not change the free energy of the reaction. It does not change what the products of a chemical reaction will be d.
Enzymes are proteins that speed up reactions by reducing the activation energy. Catalysts are not consumed in a chemical reaction they just speed up the rate of the chemical reaction without being used up. Enzymes act as catalysts.
Once all of the enzymes have bound any substrate increase will have no effect on the rate of reaction as the available enzymes will be saturated and working at their maximum rate. Enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions. An enzyme has all of the following properties except.
Endergonic Non-Spontaneous releases energy into the environment when forming a product. Blank is the intermediary molecule that captures transfers releases energy. It increases the energy yield from a chemical reaction b.
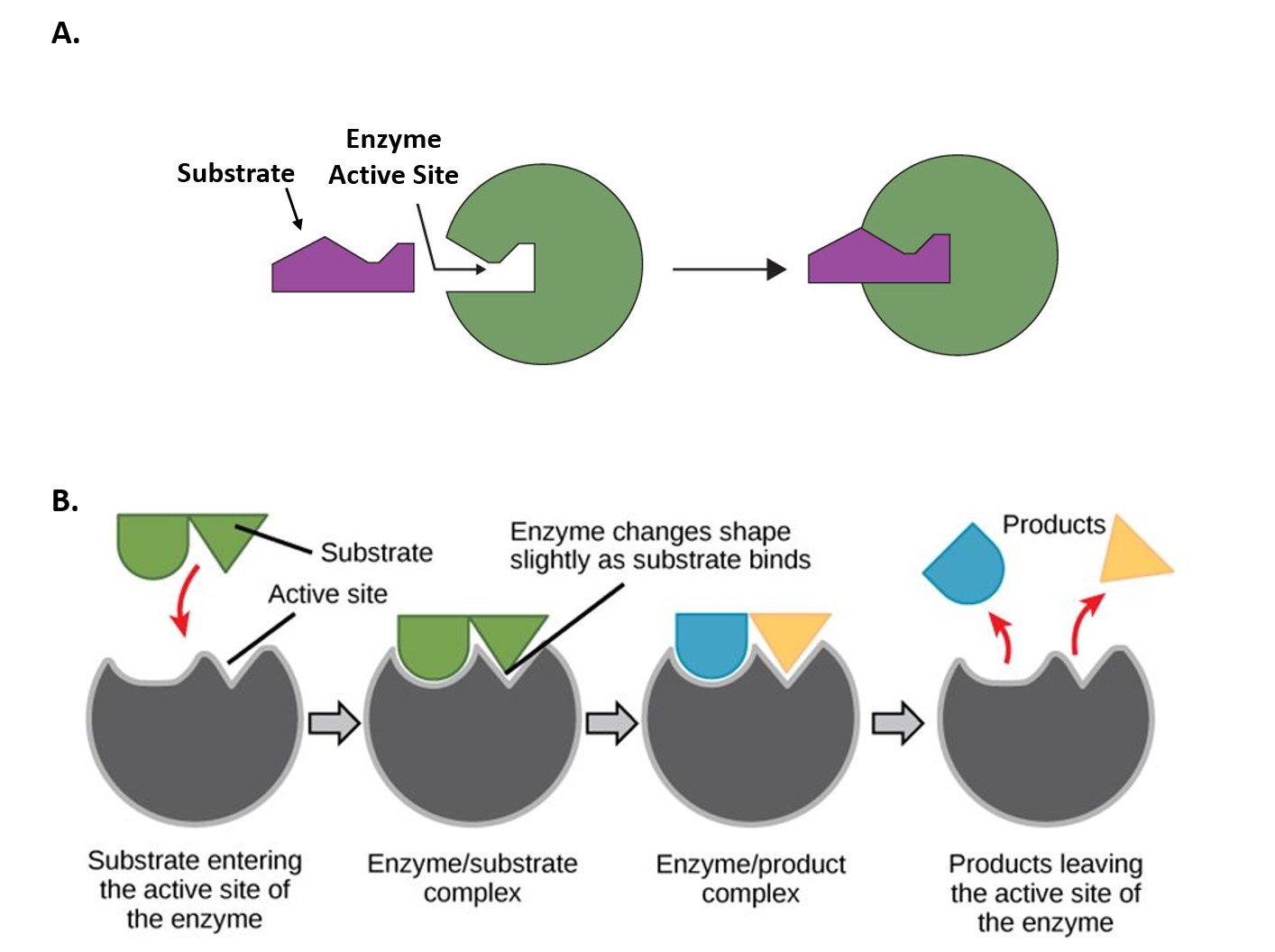
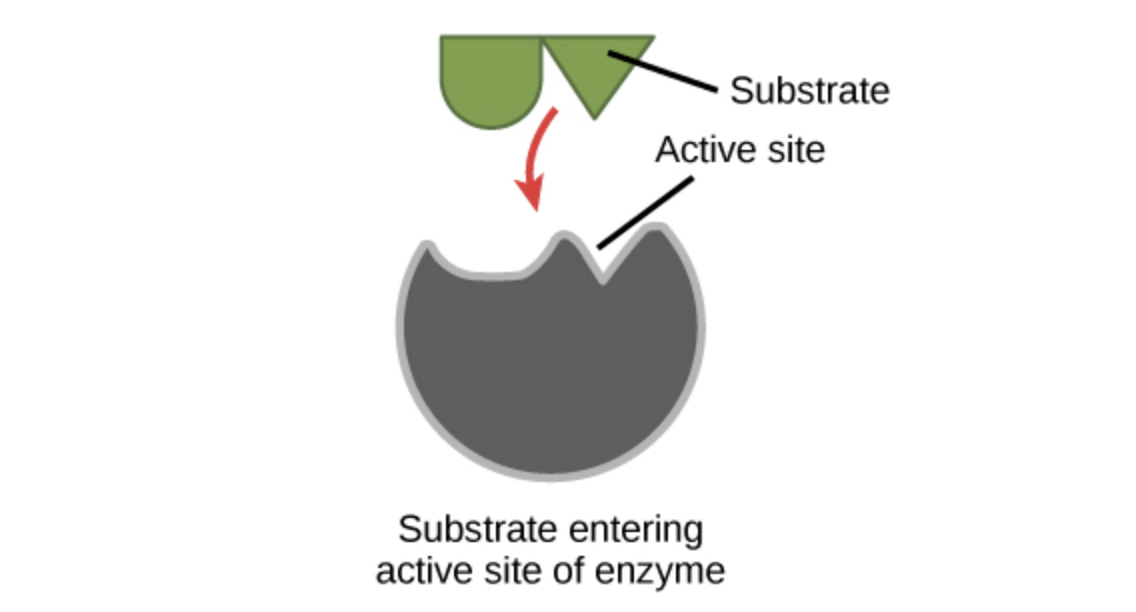
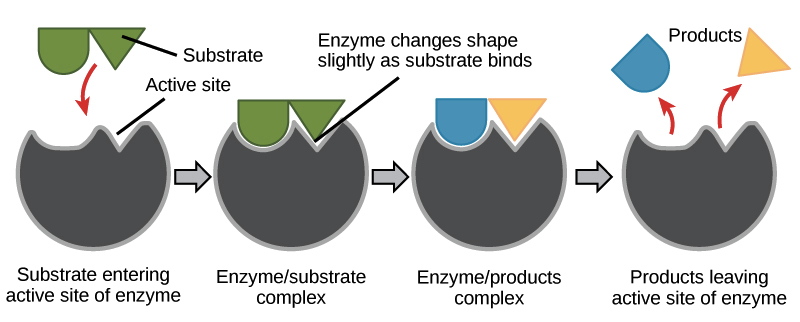
Since the catalyst is not consumed each catalyst molecule may induce the transformation of many molecules of reactants. Enzymes are designed to work most effectively at a specific temperature and pH. E S ES EP We observe that enzyme substrate complex is formed and it gives the product and the enzyme back.
Enzymes speed the reaction or allow it to occur at lower energy levels and once the reaction is complete they are again available. Absorbs utilizes energy from its surroundings to build a product. A catalyst is a chemical that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being changed by the reaction.
Since energy is always limiting in a living cell cells have adopted enzymes as a way to conserve energy. For an active catalyst the number of molecules transformed per minute by one molecule of catalyst may be. Yes enzymes can be reused over and over again for catalyzing chemical reactions because they are not consumed during the reaction so they will remain in.
An enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process. Click to see full answer.

Main Characteristics Of Enzymes In 2021 Enzymes Activity Enzymes Energy Activities
Enzymes Review Article Enzymes Khan Academy
Enzymes Catalysis And Kinetics

Home Faithful To Nature Vitamins And Minerals Vitamins Nutrition Labels

Effect Of Catalysts On Rate Of Reaction Catalyst Activationenergy Energy Activities Potential Energy Exothermic Reaction

Enzymes Biology For Non Majors I

Chloroplast Vs Mitochondria Venn Diagram Venn Diagram Mitochondria Diagram

Mitochondria Structure And Function With Diagram In 2021 Mitochondria Structure And Function Oxidative Phosphorylation
Ch103 Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions In Biological Systems Chemistry
Enzymes Review Article Enzymes Khan Academy

Mechanism Of Enzyme Action Energy Activities Biochemical Active Site

Why Do Root Hair Cells Not Have Chloroplasts Biology Quiz In 2021 Plant Cell Organelles Root

Ribosome Function And Structure What Is Ribosome Factory In 2021 Prokaryotic Cell Structure And Function Greek Words

Rate Of Reaction Enzymes Role Importance Expii

The Ping Pong Mechanism Biological Chemistry Ping Pong Cell Membrane Transport

Respiration In Plants Cbse Notes For Class 11 Biology Cbse Tuts Biologynotesclass11 Respiration Biochemistry Notes Cell Biology Notes Biology Lessons
Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy

Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy

Post a Comment for "Enzymes Are Not Consumed In Chemical Reactions What Does This Mean"