How Do Xylem And Phloem Move
Changes in diameter of a tree-during the day where transpiration rate is increased the diameter is decreased. A thick layer of cortex tissue surrounds the pericycle.

25 4b Vascular Tissue Xylem And Phloem Biology Libretexts
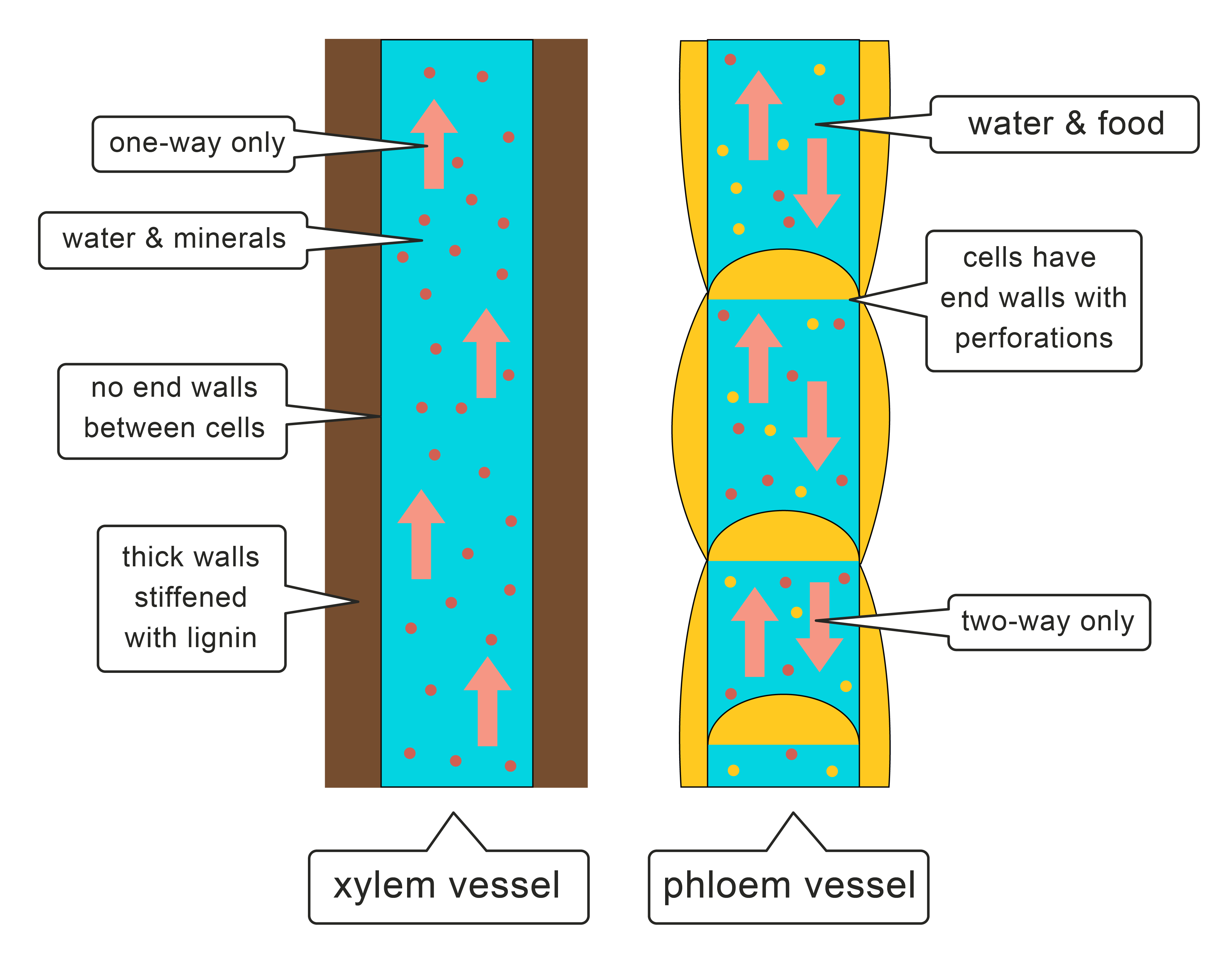
Gas bubbles in the xylem can interrupt the flow of water in the plant so they must be reduced through small perforations between vessel elements.

How do xylem and phloem move. 1-Water is passively transported into the roots and then into the xylem. Plants perform a similar function of transporting these nutrients what we know as sap by using complex tissues called xylem and phloem. The xylem moves water and solutes from th.
Xylem and Phloem - Transport in Plants Biology FuseSchoolPlants have a transport system to move things around. Plant Vascular Systems Air and oxygen is going to impact flow and create capillary action If xylem. Xylem and Phloem are two different types of vascular tissues which are mainly involved in the transportation process.
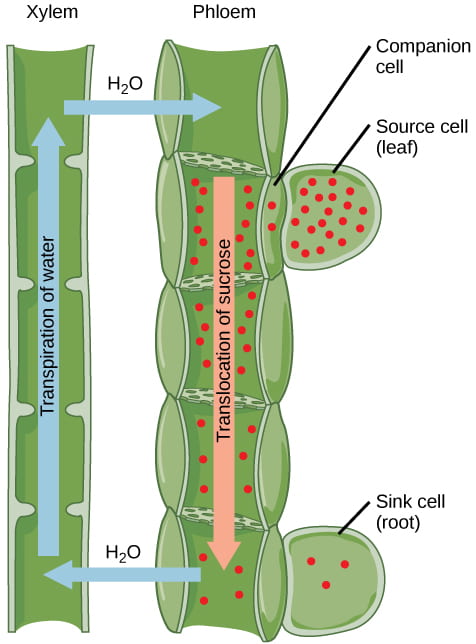
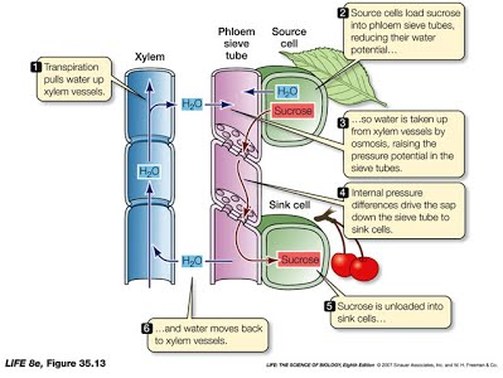
Xylem tissue transports water and mineral ions in solution. The presence of high concentrations of sugar in the sieve tube elements drastically reduces Ψs which causes water to move by osmosis from xylem into the phloem cells. These tissues form a vascular bundle and these work together as a unit.
The last process that helps water move up a stem. Xylem and phloem make network of veins supporting thin leaves. Water enters a plant through the hair on the root and moves across the root cells into the xylem which transports it up and around the plant.
Xylem on top of phloem in veins. Xylem and phloem are complex tissues as they have many functions to perform like transportation strengthening supporting the plants etc. Each vascular bundle is orientated with the xylem on the interior and the phloem on the outside of the xylem.
What does phloem tissue transport Phloem tissue mainly transports sugars also in solution both up and down the plant. During transpiration water evaporates from the leaves and draws water from the roots. The outer edge of the pericycle is called the endodermis.
In animals this function is performed by the circulatory system. The cross section of a dicot root has an X-shaped structure at its center. The innermost part of the trunk contains a xylem ie the.
These substances move up the plant from the roots to leaves. In principle either xylem or phloem could provide the plumbing through which water moves up a tree trunk or other stem. In eudicots vascular bundles are arranged in a ring within the stem.
One of the significant examples of xylem and phloem is the tree trunk. That and solutes are moved around by the xylem and the phloem using the root stem and plant. 2-The forces of cohesion and adhesion cause the water molecules to form a column in the xylem.
For instance plants like algae and mosses do not contain xylem or phloem. Xylem and phloem travel entire length of stems in discrete threads called vascular bundles. 3- Water moves from the xylem into the mesophyll cells evaporates from their surfaces and leaves the plant by diffusion through the stomata.
How are xylem vessels formed. Phloem is responsible for transporting food produced from photosynthesis from leaves to non-photosynthesizing parts of a. Which is itAn elegant experiment demonstrates which of.
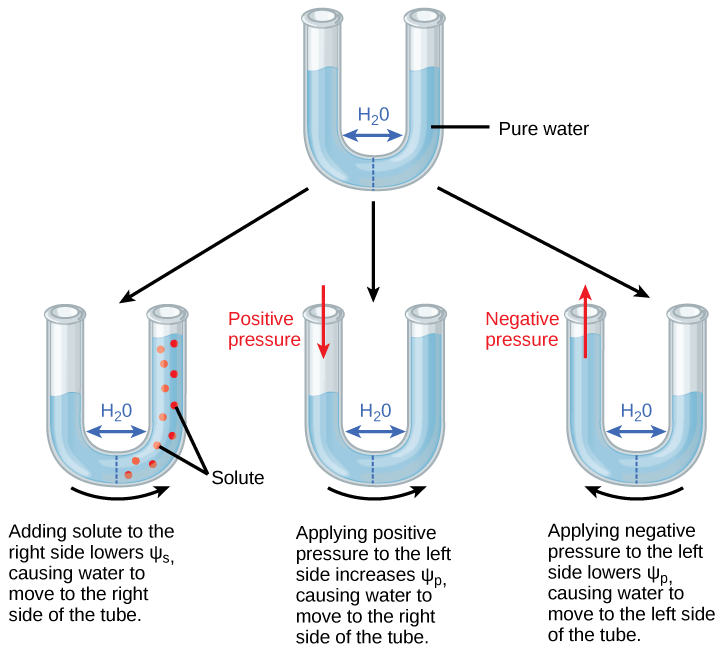
The X is made up of many xylem cells. This movement of water into the sieve tube cells cause Ψp to increase increasing both the turgor pressure in the phloem and the total water potential in the phloem at the source. View Water Potetntial xylem and phloem pdf from BIOL 1510 at Nova Southeastern University.
What is the evidence for the cohesion-tension theory. How does the xylem move water. Phloem cells fill the space between the X.
During transpiration plants move water from the roots to their leaves for photosynthesis in xylem vessels. Glucose made in photosynthesis is then moved to all cells in phloem vessels for. The xylem and the phloem make up the vascular tissue of a plant and transports water sugars and other important substances around a plant.
As you have learned earlier these two vessel systems are called xylem and phloem. Xylem is the dead permanent tissue that carries water and minerals from roots to all other parts of the plant. The movement of xylem is unidirectional while the movement of phloem is bidirectional.
A ring of cells called the pericycle surrounds the xylem and phloem. Evaporation from mesophyll cells in the leaves produces a negative water potential gradient that causes water and minerals to move upwards from the roots through the xylem. Xylem moves water from roots to the leaves and phloem moves food from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Sugar Transport In Plants Phloem Organismal Biology
How Do Xylem And Phloem Cells Differ Quora
File Flow And Exchange Of Nutrients In The Phloem And Xylem Of Plants Svg Wikimedia Commons
Which Part Of A Plant Are Xylem And Phloem Found In Quora

Sugar Transport In Plants Phloem Organismal Biology

Xylem Phloem Communication Network Control Over Nitrogen Fixation In Download Scientific Diagram

Sugar Transport In Plants Phloem Organismal Biology
Water Transport In Plants Xylem Organismal Biology
Understand The Roles Of Xylem And Phloem In Plants Worksheet Edplace
Topic 9 2 Transport In The Phloem Of Plants Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Transport Pathways Of Nutrients And Water By Xylem And Phloem In A Download Scientific Diagram
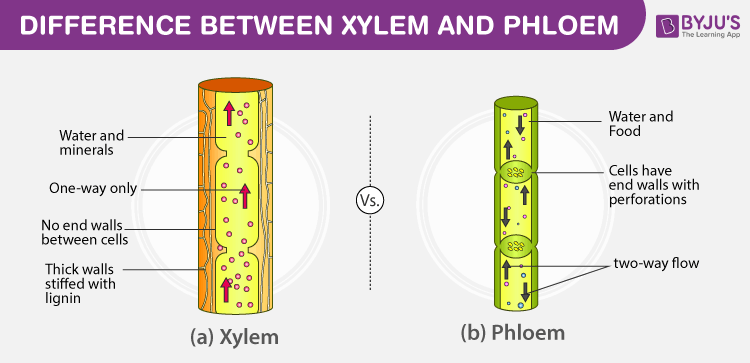
Difference Between Xylem And Phloem Major Differences
Phloem Translocation Video Khan Academy

File Flow And Exchange Of Nutrients In The Phloem And Xylem Of Plants Svg Wikimedia Commons

Plant Transportation A Closer Look At Xylem And

Phloem Vs Xylem Difference And Comparison Diffen Biology Plants Biology Plant Science
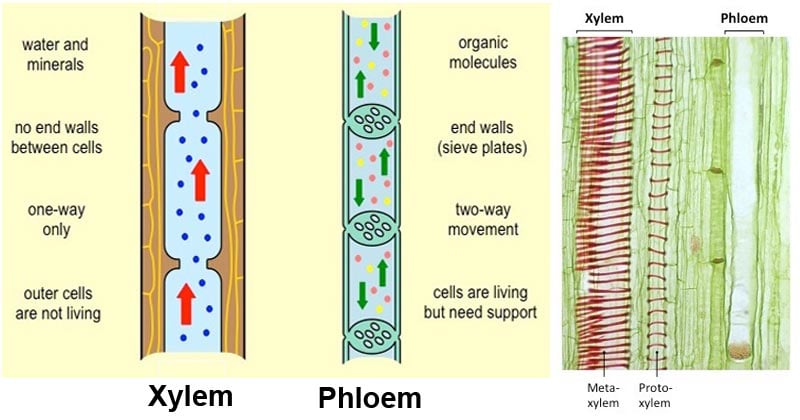

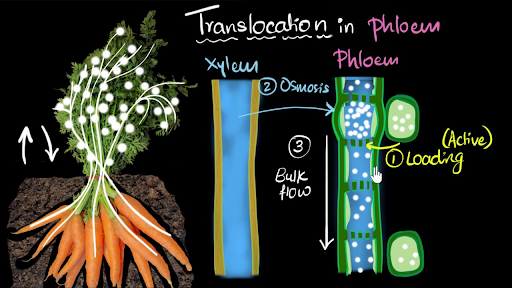
Post a Comment for "How Do Xylem And Phloem Move"